![]()
INTRODUCTION
Hello friends, I hope many points comes to your mind while reading the title of this post. Yes this post is a small post and continuation of the post Getting Started with Git Part 1 | AI Sangam. It would be great if you read the previous post so that we can be on same path. In a nutshell in the previous post there is writings on version control systems, git glossary, installing git on both windows and linux and finally git states files. Proper explanation with the screenshots is provided so that readers can also do the things practical. Same would be carried out in this tutorial also. I guess you would not skip the previous part as this is the series so you would not understand this if you would not read the last one so go and read the previous part. In this part there would be practical session on .gitignore, git diff, checkout and reset HEAD. Everything would be explained with the help of code and screenshots so if you follow me this would be great learning. I have split the git learning into many small blogs so that readers can read and practice things in chunks and better learning can be achieved. Let us see the table of content from below
TABLE OF CONTENT
Ignoring files in git
There may be some files which one needs not to be tracked by git. Let us create a directory in the local computer. I have created a folder named as github in my system and then went inside the folder github. Open terminal and execute the below command
git init
This will enable this directory to be treated as git directory. Now create two files named as FileAISangam.yml and FilePython.py. If you want to ignore the file FileAISangam.yml and does not want it to be tracked by git, please create a new file in the directory named as .gitignore and put the name of the file you want to ignore (FileAISangam.yml). See the screenshot before adding this file to .gitignore
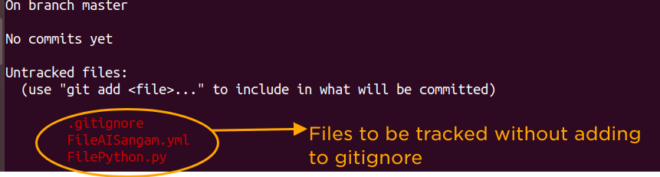
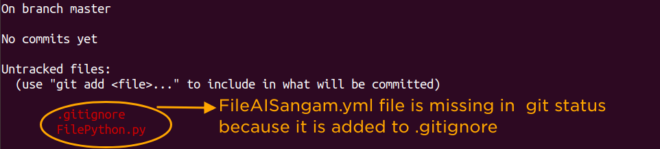
See the screenshot after adding the file FileAISangam.yml to .gitignore
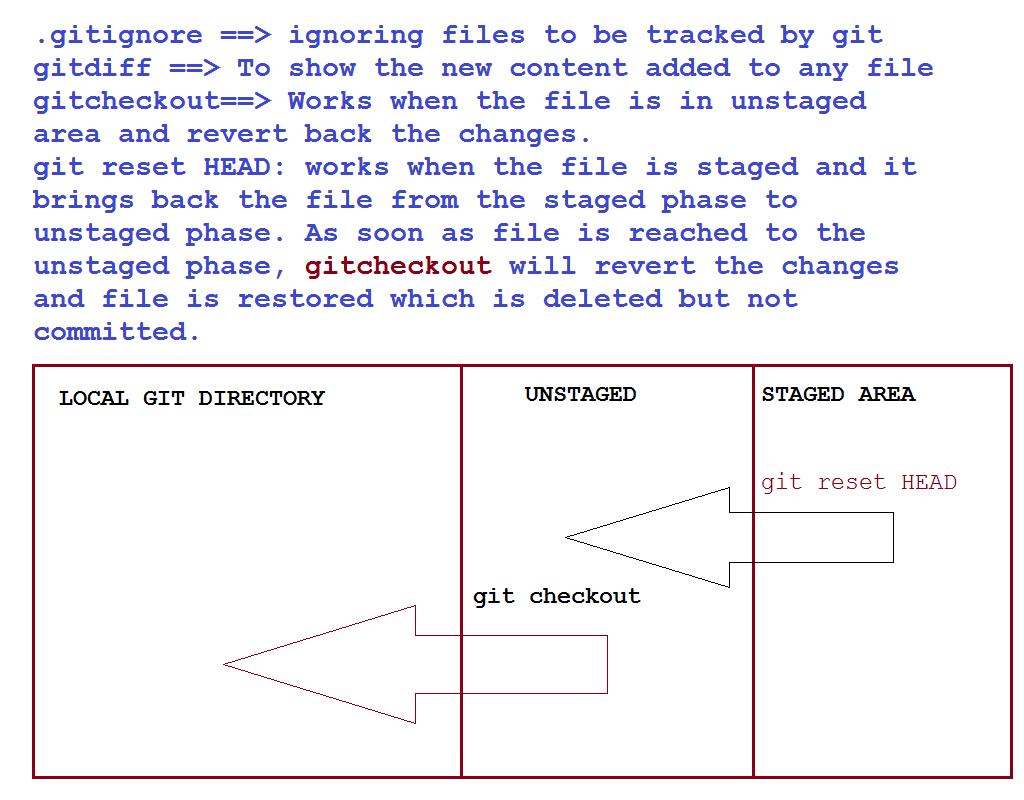
git diff and git checkout
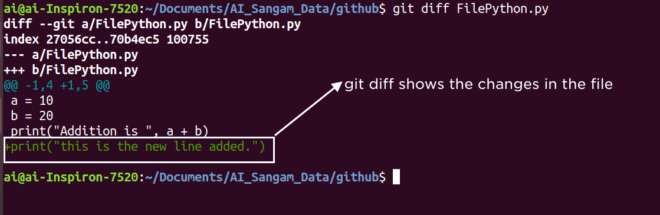
git diff is used to show the changes in any file. Let us add some text in the file FilePython.py and one can see that what are the new changes reflected in the file. Please see the below screenshot to see the new changes.
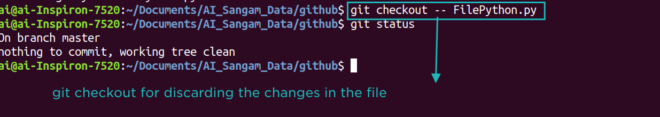
git checkout: Now suppose, one have to discard the changes done in the previous step like you can see the changes shown using git diff command. In this case instead of git add you have to execute the following command
git checkout -- name of file
Please see the below screenshot to understand this step in more refined way.
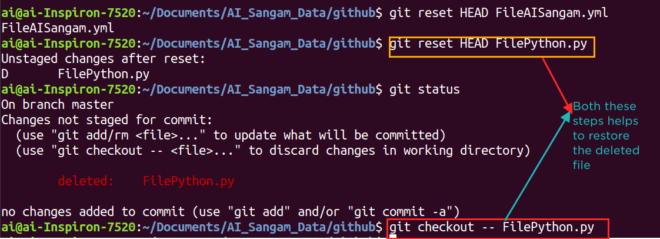
git reset HEAD
This command is used to bring the deleted file back from the staged area to unstaged area. Once the file is brought back, it is important to restore the file which one can do using git checkout. Let us see these two commands using the screenshot. Suppose I have deleted the file FilePython.py using the command sudo rm FilePython.py. In order to restore this file, I have run the commands as shown in the below screenshot
Bottom Line
As the tutorial progressed we have seen how the commands such as .gitignore, git checkout and git reset HEAD works. These commands are very important and hence all the commands are explained with proper care, code and screenshots. I hope everything will help to gain better insights. I also urge readers to read the previous tutorial as this is part 2 of the series. If you have not read it, please read it from the below link
Getting Started with Git Step by Step Part 1 | AI Sangam
If you wish like to write an feedback to us, you may either do it in the comment section or can also email us at aisangamofficial@gmail.com. It would be modest from your side, if you can watch some of our videos at AI Sangam official you tube channel. You may also reach us at skype using the id aisangamofficial. Thanks for reading this post. Stay with us tuned for the next article of this series.
You can also go back from here and see the first part of the series

Shakshi this side,
Hello AI Sangam, I would like to share my knowledge on different options with git add as I hope this would also help readers.
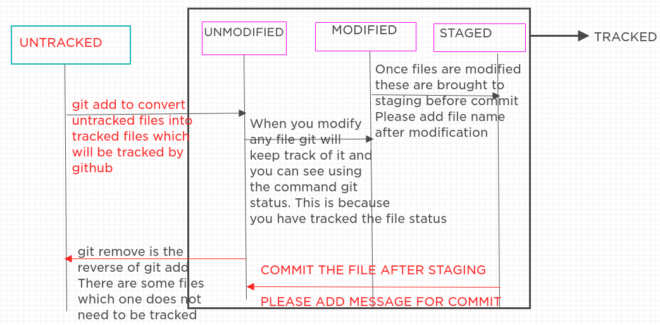
git add . = This will add new as well as modified files but not the deleted files.
git add -u = This will add modified and deleted files but not new files.
git add -A = This will add files whether deleted, newly created or modified.
Thanks a lot for sharing this valuable point. I hope you have good knowledge of git.